African Research Journal of Education and Social Sciences, Vol., 2, 2015
Author: Julia Kendi Muriithi
<Department of Commerce and Economics, School of Human Resource Development, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology- Mombasa Campus, P.O Box 31-00600, Nairobi- E-mail: kendiblanche@gmail.com>
Fred Mugambi Mwirigi
<Director, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Mombasa Campus, P.O Box 81310-80100, Mombasa-Kenya. Email: fmgambi@gmail.com>
Abstract
The main purpose of this research was to examine the challenges faced in managing resistance to change with reference to a securities industry in Kenya. The research employed a descriptive research design. The sample consisted of six (6) top level managers of the institution and forty two (42) members of support staff. In total, there were forty eight (N=48) respondents. Census method was used to arrive at the sample. This was to ensure inclusiveness. Questionnaires and interview guide were used to collect data from the respondents. Quantitative and qualitative approaches were used for data analysis. Quantitative data from the questionnaire were coded and entered into the computer for computation of descriptive statistics with the help of SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Science). The research showed that there are certain mindsets that negatively influence the management of resistance to change. Some of these mindsets include but not limited to disengagement, misidentification and disenchantment. The research also revealed that lack of effective communication among the managers and employees as another factor that affected the management of resistance to change. Lack of adequate resources also hampered the staff members from accepting change at the institution. The research recommended that the institution’s management to develop a sense of good relations with the employees and ensure that effective communication between them ensued; the management to also encourage employee development in the change process. The research also recommended the management to actively engage the employees in the change process and to introduce the aspired changes in phases.
Key words: Resistance Management, Resistance to Change, Managing Resistance to Change, Resistance Management Challenges, Change Management, Employee Resistance
1. Introduction
Change is inevitable; it remains the only constant reality (Smith, 2004). In order to adapt to the demands of clients and the general market, organizations as well as individuals are forced to undergo various changes (Nilakant & Ramnarayan, 2006). However, despite the fact that change is an organizational process aimed at empowering employees to accept and embrace changes in their current business environment (Hiatt, 2010), there are still several predicaments that are experienced (with resistance being one of them) while implementing organizational change.
In Africa, institutions and organizations are going through a very difficult time. This has been occasioned, in part, by unfavorable external events, often beyond the immediate control of these organizations. Further, the current wave of global competition, brought about by economic and political liberalization in most countries, and the local companies ‘comparative disadvantage vis-à-vis well established multinational organizations in areas such as technology, market information, and access to sources of raw materials, and worker productivity are some of the challenges African managers have to deal with (Mbano, 2000).
In Kenya, the issue of resistance to change is not quite different from what has been happening in the continent. In the Kenyan securities industry, the management of change has been occasioned by the fluctuations in the securities industry and mergers. The challenge may not only be to the support staff but to the very managers of change. This research examines the theme of managing resistance to change with reference to one securities industry located in the heart of Nairobi, Kenya.
2. Objectives of the Research
In order to respond to some internal and external problems, the securities industry had to go through various strategic changes. However, the ‘receivers’ of change do not always receive it with open hands as it threatens their stability in the organization. Therefore, this research intended to examine the major challenges faced in the management of resistance to change with reference the securities industry.
The research was guided by the following specific objectives:-To analyze how the mindset of the employees on change affect the management of resistance to change in the securities industry in Kenya, to establish the extent to which lack of resources affect the management of resistance to change in the securities industry and to determine how the perception of the top management affect the management of resistance to change in the securities industry.
3. Research Design and Methodology
This research employed descriptive research design which has evolved over the past years as useful tool for an in-depth investigation of trends and specific situations. This research used census survey sampling procedure to obtain the respondents for questionnaires and interviews. This research collected data from all respondents consisting of all forty two (42) support staff members and all six (6) top managers at the securities industry. The contribution of each of the participant on the challenges faced in the management of resistance to change was deemed vital towards answering the research problem. In total, the sample were forty eight respondents (N=48). Purposive sampling procedure was used to pick the top managers.
The questionnaire was used to collect data from the support staff members. It was divided into the main areas of investigation except the first part which captured the demographic characteristics of the respondents. Other sections were organized according to the major research objectives. On the other hand, interview method was used to collect primary, qualitative data from the top management. The interview guide was semi-structured (with some closed and open ended items). It was divided into two main sections, namely demographic characteristics and the challenges faced in the management of resistance to change.
Both quantitative and qualitative approaches were used in data analysis. Quantitative data from the questionnaire were coded and entered into the computer for computation of descriptive statistics. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS version 11.5) was used to run descriptive statistics such as frequency and percentages so as to present the quantitative data in form of tables and graphs based on the major research questions. The qualitative data generated from interview guide was categorized in themes in accordance with research objectives and reported in narrative form along with quantitative presentation. The qualitative data was used to reinforce the quantitative data. The conclusions and recommendations were derived from the results of the analysis.
4. Identified Challenges
The key challenges addressed in the reviewed studies included: mindset of employees, provision of resources and the top management issues. Additionally, some of these studies reviewed have also addressed on some of the measures and strategies that can be put in place to counter the challenges faced in the management of resistance to change in organizations. Along this line a recent research by Allred (1987) holds the view that where employee mindset is concerned, individuals with experience performing a specific task tend to resist change more than individuals with less experience. It is therefore very important for the management to create awareness concerning the change process anticipated in the Organization before it actually happens.
Pettas and Gilliland (1992) originally implied that inept management resources can cause resistance to change to accelerate. Both logic and research support this statement and show us the need for resources to be availed to manage change resistance. An organization should provide adequate resources to supplement the change efforts and being generally sensitive to the resources that employee need to push the agenda of change. Committing sufficient resources to the change to ease the transition process and alleviate employee frustration is prerequisite for effective change management.
5. Results
The results are organized based on key research themes except the first part which presents the background information. These themes include effect of employees mind set on the management of resistance to change, extent to which lack of resources affect the management of resistance to change, how the top management affect the management of resistance to change. The last part presents the key strategies which can be adopted to address the challenges in change management.
5.1 Background Characteristics
Majority of the staff members, 32 (76.2%) who participated in the research had attained degree level of education. However, a few of them, 6 (14.3%) had masters level of education. The dominance of degree holders in this organization may be attributed to the fact that the institution being a securities industry requires people who are well educated.
Slightly less than a half of the staff members, 19 (45.3%) indicated Customer service and Sales as their designation. However, 6 (14.3%) of them indicated that they belonged to the Operations Department, while 4 (9.5%) of the employees stated they were in the Agency department. Other designations listed included Finance 6 (14.30%), Research 4 (10%) and legal 3 (7.10 %) section respectively.
With regard to academic qualification, all the six top managers were holders of Master’s degree. Each of the managers headed Operations, Research, Finance, Legal, Customer service & Sales and Agency departments.
5.2 Effects of Employees’ Mind Set on the Management of Resistance to Change
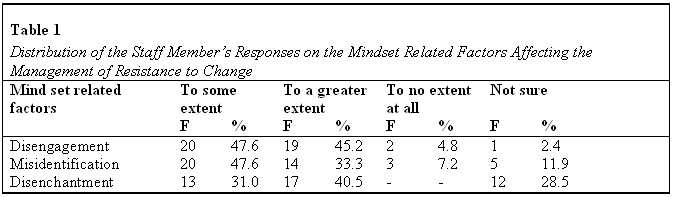
In the implementation of any change in an organization, the mindset of employees towards the change plays a critical role. If the mindset of employees is not into the change, it is hard to implement the change or manage it. This study sought to establish how the mindset of the employees affected the management of resistance to change in one selected securities industry. The staff members were asked to give their views on the extent to which various mindset related factors affected the management of resistance to change in their respective departments in the institution.
Asked to indicate the extent to which disengagement factor affected the management of resistance to change, an overwhelming majority of the staff members, 39 (92.8%) were positive that it affected either to some extent or to a greater extent. However, only two of them (2) indicated that disengagement affected the management of resistance to change to no extent.
With reference to the misidentification, slightly less than a half of the staff members, 20 (47.6%) indicated that misidentification affected management of resistance to change to some extent.
Additionally, a third of them, 14 (33.3%) also indicated that the misidentification mindset factor affected the management of resistance to change to a greater to a greater extent.
In terms of the disenchantment factor, majority of the staff members, 30 (71.5%) were positive that disenchantment affected the management of resistance to change either to some extent or to a greater extent. However, slightly more than a quarter of them, 12 (28.5%) were not sure.
The respondents were further asked to indicate whether they were familiar with some of the factors that influenced them to resist change in the institution. Slightly more than half of the staff members, 24 (57.1%) agreed that surprise and fear of the unknown was one of the factors that influenced employees to resist change in an organization. However, 42.9 % of them indicated that surprise and fear of the unknown did not influence them to resist change.
With reference to the Mistrust Factor, a majority of the staff members, 28 (66.7%) indicated that this factor did not influence them to resist change in the organization. However, a third of them, 14 (33.3%) indicated that the factor had some level of influence.
In terms of the fear of failure, slightly more than a half of the staff members, 22 (52.4%) indicated that the fear of failure did not influence them to resist change in the organization. However, 47.6% of them indicated that indeed, the fear of failure made them to resist change on the institution.
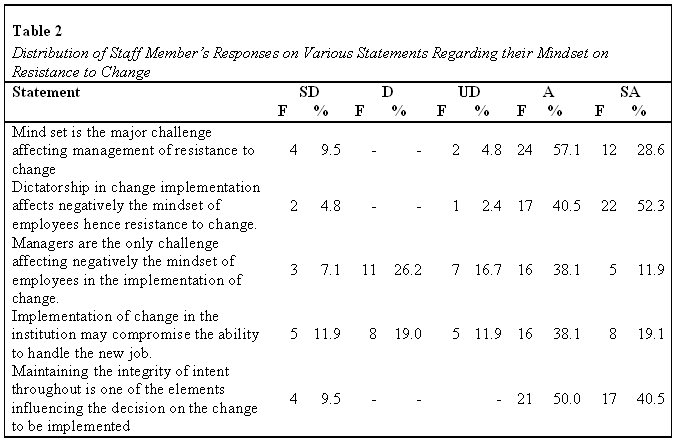
The staff members were further asked to indicate whether they Strongly Disagreed (SD), Disagreed (D), Undecided (UD), Agreed (A) or Strongly Agreed (SA) to the following statement regarding the employees mind set and management of resistance to change.
Asked whether the mindset was the major challenge that affected the management of resistance to change, a majority of the staff members, 36 (85.7%) indicated that employee mindset was indeed the contributing factor of change resistance among the staff.
Slightly more than a half of the staff members, 22 (52.4%) strongly agreed that the management use of dictatorship in the implementation of change had a negative influence hence resulting to resistance to change. This was further confirmed by 40.5% of the staff members who also agreed that the style of leadership negatively affected the mindset of employees hence the resistance to change in the institution.
Asked to indicate whether managers were the only source of challenge that negatively influenced mindset of employees in the implementation of change, half of the staff members 21 (50%) were positive by either strongly agreeing or agreeing to the statement. However, a third of them 14 (33.3%) were negative by strongly disagreeing or disagreeing to the statement.
In terms of compromised abilities to handle new jobs, slightly more than a half of the staff members 24 (57.1%) either strongly agreed or agreed to the statement that the implementation of change in the institution could compromise their ability to handle the new job hence developing a negative mindset towards the change. However, slightly less than a third of them, 13 (30.9%) disagreed that their resistance to change was not based on compromised abilities to handle new jobs.
Majority of the members of staff, 38 (90.5%) agreed that maintaining the integrity of intent throughout was one of the elements that influenced their decision on the change that was to be implemented in the organization. A few of them, 4 (9.5%) however differed.
When the top managers were interviewed on how the mindset of the employees affected the management of resistance to change most of them reported that indeed there were a couple of employees’ mindset related factors that affected them during the management of resistance to change in the institution. Some of these factors that they reported included the climate of mistrust due to past history of change in the organization, fear of failure, threat to their current positions as a result of upcoming change in the organization and the change in the organizational culture.
5.3 Extent to Which Lack of Resources Affects the Management of Resistance to Change
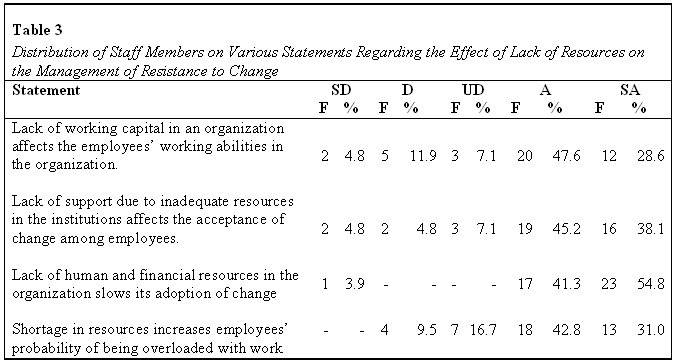
This research sought to establish the extent to which lack of resources affected the management of resistance to change in the targeted securities industry. The staff members were asked to indicate whether they Strongly Disagree (SD), Disagree (D), Undecided (UD), Agreed (A) or Strongly Agreed (SA) to the various statements on the effect of lack of resources on management of resistance to change. Table 3 shows the distribution of the respondents’ responses.
Majority of the staff members, 32 (76.2%) either strongly agreed or agreed that lack of working capital affected the employees’ working abilities in the organization. However, a few of them, 7 (16.7%) disagreed that lack of working capital affected their working abilities in the organization.
An overwhelming majority of the staff members, 35 (82.2%) either strongly agreed or agreed that lack of support due to poor resources in the organization negatively influenced the acceptance of change among employees. With reference to the work overload due to limited resources, a majority of the staff members, 31 (73.9%) either strongly agreed or agreed that shortage in human resources increased the employees probability of being overloaded with work if change in implemented.
When the top managers were asked to explain whether there were adequate resources that supported the implementation of change in the organization, they all reported that there were no adequate resources in the organization to support not only the implementation of change but also the management of the resistance to change.
The managers were further asked to explain the extent to which the unavailability of resources in the organization hindered the management of resistance to change. One of the managers reported that to some extent, the unavailability of resources in the organization brings about a challenge when I am implementing or trying to manage any resistance to change among the staff. Thus is lack of adequate resources ends up prolonging the implementation of change process (Top Manager II, 2012).
5.4 Effects of Top Management Perception on the Management of Resistance to Change
This research sought to establish how the perception of the top management affected the management of resistance to change in the selected institution. The staff members were asked to indicate whether the top management related issues affected the management of resistance to change in the organization or not.
There are a couple of top management related issues that affect the management of resistance to change. From the findings, a majority of the staff members, 27 (64.3%) indicated that poor communication skills among the top management was the key management issue that negatively influenced the management of resistance to change. Another issue that was brought across by 64.3% of staff members was their poor relationship with the staff members.
The views of the top management coincided with those of the staff when they pointed out that there are a number of factors that affect the management of resistance to change in the institution. These included lack of proper communication, poor relation between the staff members and management team, internal politics within the organization, negative attitude of managers towards changes that are being introduced, lack of adequate training among the managers on the change being implemented and fear of losing positions of influence as a result of new changes being introduced in the organization.
6. Discussion
The mindset of employees or any organization’s staff is a crucial element for an effective change in the organization. Under this section, the research found that the employee mindset affected to a larger extent the management of the resistance to change at the securities industry investigated. The research established that employees at the institution had certain mindset such as disengagement, misidentifications and disenchantment. This type of mindset on the side of employees means that employees are not ready both physically and psychologically to embrace the expected organizational changes. And this, as the research further established hampered greatly the management of the resistance to change at the institution.
The findings of this research are consistent with the earlier findings by Huczynski and Buchanan (2004). In their research on how the mindset of the workers can influence organizational changes, the researchers established that employees who were disengaged in work were less effective in implementing the organizational changes. Other factors noted in this research were misidentification and disenchantment. Apparently, the research established that lack of effective communication among the managers and employees was another factor that affected the management of the resistance to change in the institution. Another factor was fear of failure among the employees. This may be attributed to the fact that the employees may not be conversant with the new perspective of things in the organization especially whose experience in working in the institution is wide.
An organization should provide adequate resources to supplement the change efforts and being generally sensitive to the resources that employee need to push the agenda of change. Committing sufficient resources to the change to ease the transition process and alleviate employee frustration is prerequisite for effective change management. This research sought to examine the extent to which lack of resources affected the management of the resistance to change in the selected securities industry. Results demonstrated that lack of resources (especially human and financial was a key factor that hampered staff members from accepting change at the institution. Lack of adequate working capital for instance was said to affect the employees’ working abilities in the organization thus further compromising the management of the resistance to change in the institution.
Fine (1986) suggests that in many organizations, it is not uncommon for resources (particularly personnel resources) to be overextended or withdrawn just when staff is experiencing the greatest stress of change. Further, she contends that administrators often skimp on really necessary items, for instance complete training by experts may be viewed as an extravagance rather than as a necessary expenditure associated with change. Thus, it is important for managers to be particularly sensitive especially when dealing with change management. They should critically examine if they have supported the innovation by providing all necessary resources, be it money, time, increased attention to detail by management, and added personnel.
The findings of this research are consistent with earlier revelations that, managers have always contributed to efforts that lead to resistance to change in institutions (Pettigrew & Whipp, 1991). This research established that top management issues at the institution affected the management of resistance to change to a great extent. Some of the management issues pointed out by majority of the respondents that affected the management in the resistance to change included poor communication skills among the managers and poor relation with staff members. In addition, internal politics within the company, negative attitude of managers towards changes that are introduced, and lack of training on the change implementation process and fear of losing positions of influence were also the management related issues that affected the management of resistance to change at the institution.
Morrison and Milliken (2000) observe that unless the management prepares the support staff emotionally for change, the sheer speed, severe communication breakdown by the management and a lack of coordination in the process of change management in an organization is the main cause of change difficulties. Greenhalgh, Worpole and Landry (1995) also add that managers have to handle all the challenges of change simultaneously, which requires good coordination, strong leadership, and clear communication.
7. Conclusions
The following conclusions are based on the key findings of the research and in line with the major research objectives.
In terms of the employees’ mindset in the management of resistance to change, it can be concluded that there are certain mindsets that negatively influence the management of resistance to change. Some of these mindsets included disengagement, misidentification and disenchantment. Further, the research established that lack of communication among the managers and employees was another factor affecting the management of the resistance to change in the institution. Managers ought to communicate to employees and inform them on any new changes to be introduced in the organization, who will be affected and how this may affect their roles in the organization to enable employees to be open to change.
Lack of resources was another factor that hampered staff members from accepting change at the institution. This issue also affected employee’s acceptance to change in the organization. Apparently, lack of working capital in the organization also affected the employees’ working abilities in the organization thus decelerating the change process. Thus, human and financial resources are essential for effective management of the change process in the institution.
The research further concluded that the top management at the institution affected the management of resistance to change to a great extent. Some of the management issues such as poor communication skills among the managers and poor relation with staff members, internal politics within the company, negative attitude of managers towards changes that are introduced, lack of training on the implementers of the change process and fear of losing positions of influence affected the management in the resistance to change in the institution.
8. Recommendations
Based on the key findings, the research recommends the following:- Managers to take responsibility of implementing change as opposed to delegating it as an HR function, top management to cultivate good relationship with staff members and ensue good communication, employees to be encouraged to share their views with the management without fear of reprisals, the organization to ensure that the opinion of the staff members does not jeopardize their jobs, the management to provide a conducive working environment for the employees, the management to plan for the training of the employees on any change process being undertaken in the institution, the management to encourage team work among the employees, the management to be friendly while dealing with the middle level and bottom level staff members and lastly the institution to engage the staff members in the change process and incorporating their opinions.
9. Recommendation for Further Research
This research did not tie the resistance to change with organizational performance. Thus, there is need to undertake another research to examine the effect of resistance to change on organizational performance.
References
Allred, C. B. (1987). The anatomy of conflict: some thoughts on managing staff Conflict. Law Library Journal, 79 (1), 7-32.
Fine, S. F. (1986). Technological innovation, diffusion and resistance: A historical Perspective. Journal of Library Administration, 7, 83- 108.
Folger, R., & Skarlicki, D. (1999). Unfairness and resistance to change: hardship as Mistreatment, Journal of Organizational Change Management, 35-50.
Greenhalgh, L., Worpole, K., & Landry, C. (1995). Libraries in a world of resources. London: UCL
Hiatt, J. (2010). The definition and history of change management. Retrieved from http://www.changemanagement.com/tutorial-definition-history.htm
Huczynski, A.A., & Buchanan, D. A. (2004). Organizational Behaviour: An Introductory Text (5 Ed.). Upper saddle River, New Jersey: Financial Times Prentice Hall.
Kilonzo, S. (2008). The Global Financial Crisis: It’s Impact on Kenya and Possible Strategies to Mitigate the Effects. Retrieved from http://www.cma.or.ke/index.php?option=com_docman&task.
Mbano, V. (2000). Challenges facing manager in Africa. Retrieved from www.web2.msm.nl/articles/
Morrison, E.W., & Milliken, F. J. (2000). Organizational silence: a barrier to change and development in a pluralistic world. Academy of Management Review, 25 (4), 706-725.
Nilakant, V., & Ramnarayan, S. (2006). Change Management: Altering Mindsets in a Global Context. New Delhi: Response Books.
Pettas, W., & Gilliland, S. L. (1992). Conflict in the large academic library. Journal of Academic Librarianship, 18 (1), 24-29.
Pettigrew, A., & Whipp, R. (1991). Managing Change for Competitive Success. Blackwell Publishers:Oxford.
Smith, A.C.T. (2004). Complexity theory and change management in sport organizations. Emergence: Complexity & Organization, 6 (1-2), 70-79.
Citation
Kendi, J., & Mugambi, F. (2015). Challenges of Managing Resistance to Change in Kenya’s Securities Industry: Lessons from a Developing Economy. Africa Research Journal of Education and Social Sciences (ARJESS), Vol., 2, 2015, http://arjess.org/social-sciences-research/challenges-of-managing-resistance-to-change-in-kenyas-securities-industry-lessons-from-a-developing-economy/